Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common hormonal disorders affecting women of reproductive age. Despite its prevalence, PCOS remains widely misunderstood, often leading to misdiagnosis, delayed treatment, and unnecessary suffering. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the intricacies of PCOS, exploring its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and management strategies to empower women with knowledge and understanding.
What is PCOS?
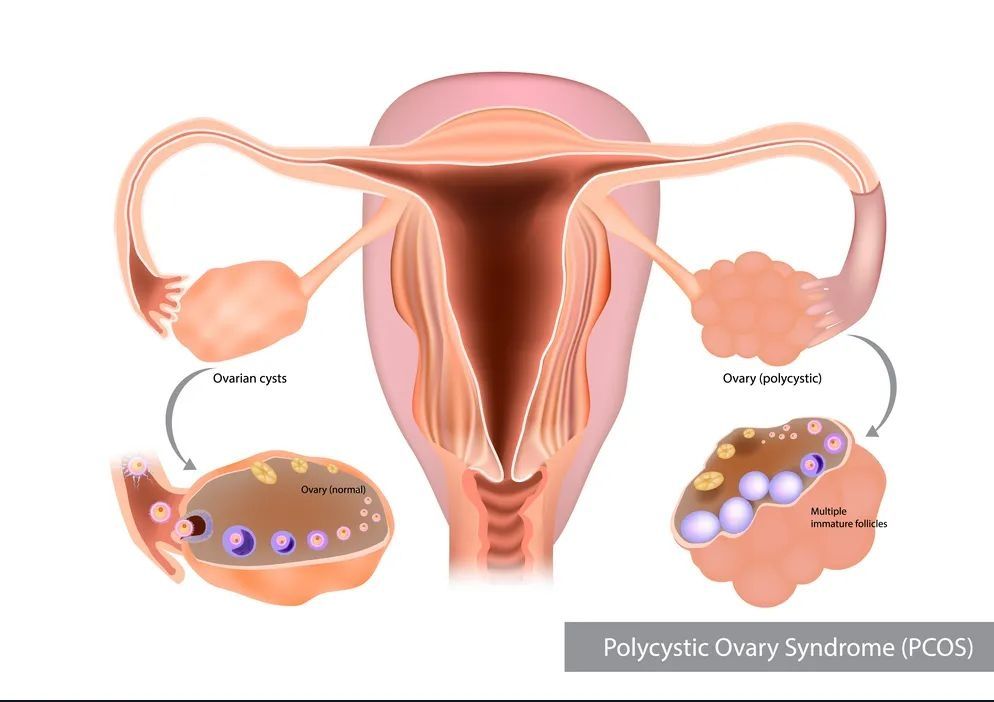
PCOS is a complex hormonal disorder characterized by a combination of symptoms, including irregular periods, ovarian cysts, hormonal imbalances, and metabolic disturbances. While the exact cause of PCOS remains unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Symptoms of PCOS
The symptoms of PCOS can vary widely among individuals, making diagnosis challenging. Common signs and symptoms of PCOS include:
1. Irregular menstrual cycles or absence of menstruation
2. Excessive hair growth (hirsutism) on the face, chest, or back
3. Acne or oily skin
4. Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
5. Thinning hair or hair loss on the scalp
6. Darkening of the skin, particularly in skin folds such as the neck or groin (acanthosis nigricans)
7. Difficulty conceiving (infertility) due to irregular ovulation or lack of ovulation.

Diagnosis of PCOS
Diagnosing PCOS requires a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. There is no single test to diagnose PCOS, but healthcare providers typically look for a combination of criteria, including:
1. Irregular menstrual cycles or anovulation
2. Clinical or biochemical signs of hyperandrogenism (elevated levels of male hormones)
3. Ovarian cysts detected on ultrasound imaging
Treatment Options.
While there is no cure for PCOS, effective management strategies can help ease symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment options for PCOS may include:
1. Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and stress management exercises like yoga and box breathing can help improve symptoms and promote overall well-being.
2. Medications: Hormonal contraceptives, anti-androgen medications, and insulin-sensitizing drugs may be prescribed to regulate menstrual cycles, manage symptoms of hyperandrogenism, and improve insulin resistance.
3. Fertility treatments: Women trying to conceive may benefit from medications to induce ovulation or assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
4. Management of metabolic complications: Addressing metabolic abnormalities such as insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and obesity through lifestyle modifications and medications can help reduce the risk of long-term health complications such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Education and awareness are powerful tools in the fight against PCOS. By understanding9 the signs, symptoms, and management strategies associated with PCOS, women can advocate for their health, seek timely medical intervention, and make informed decisions about their care.
PCOS is a complex and multifaceted condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and management. By raising awareness, promoting early detection, and providing compassionate care, we can empower women with PCOS to lead fulfilling lives and achieve optimal health and well-being. Together, let’s break the silence surrounding PCOS and support women on their journey to empowerment and wellness.

Leave a comment